o To study about transceiver (Transmitter & Receiver)
o To study about Radio Frequency (RF)
Activities : On this week, i have study and do some research about the wireless system, RF transmitter & RF receiver. It is because in my project, i use this RF features to create a wireless network. I can change the frequency according to the required distance by using RF (Radio Frequency) system.
Analysis : The details of my research are shown above:
WIRELESS, TRANSCEIVER & RF:
Wireless
The word wireless is dictionary defined as "having no wires". In networking terminology, wireless is the term used to
describe any computer network
where there is no physical wired connection between sender and receiver, but
rather the network is connected by radio waves and/or microwaves to maintain
communications.
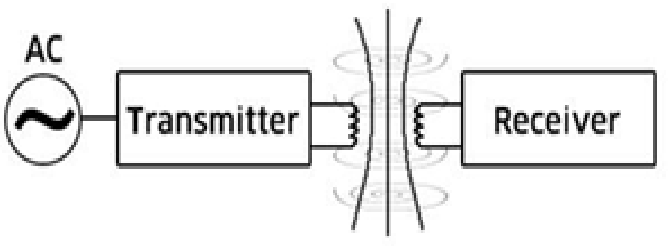
Transceiver
Transceiver is short for transmitter-receiver, a
device that both transmits and receives analog or digital signals. The term is
used most frequently to describe the component in local-area networks
(LANs) that actually applies signals onto the network wire and detects
signals passing through the wire. For many LANs, the transceiver is built into
the network interface card (NIC). Some types of networks, however, require
an external transceiver. In Ethernet networks, a transceiver is also
called a Medium Access Unit (MAU). In radio communications, a transceiver
is a two-way radio that combines both a radio transmitter and a receiver that
exchanges information in half-duplexmode.
RF (Radio Frequency)
Short for radio frequency, any
frequency within the electromagnetic spectrum associated with radio wave
propagation. When an RF current is supplied to an antenna, an electromagnetic
field is created that then is able to propagate through space. Many wireless
technologies are based on RF field propagation. These frequencies make up part
of the electromagnetic radiation spectrum:
- Ø Ultra-low frequency (ULF) -- 0-3 Hz
- Ø Extremely low frequency (ELF) -- 3 Hz - 3 kHz
- Ø Very low frequency (VLF) -- 3kHz - 30 kHz
- Ø Low frequency (LF) -- 30 kHz - 300 kHz
- Ø Medium frequency (MF) -- 300 kHz - 3 MHz
- Ø High frequency (HF) -- 3MHz - 30 MHz
- Ø Very high frequency (VHF) -- 30 MHz - 300 MHz
- Ø Ultra-high frequency (UHF)-- 300MHz - 3 GHz
- Ø Super high frequency (SHF) -- 3GHz - 30 GHz
- Ø Extremely high frequency (EHF) -- 30GHz - 300 GHz


No comments:
Post a Comment